Achalasia Cardia Treatment in India
Plan your Achalasia Cardia Surgery in India with Tour2India4Health Consultants
Achalasia Cardia Surgery in India aims to decrease LOS resting pressure without completely compromising its competency against the gastroesophageal reflux (GOR). Surgeons and other medical practitioners in India stand #1 in their respective field. Our hospitals have state-of-art equipment that increase success rate of treatments. Tour2India4Health is a medium to make these immaculate services accessible to patients from any corner of the world. We offer low cost achalasia cardia surgery at the best hospitals in India.
How things function at Tour2India4Health Group:
- Top 10 hospitals in India: India has a wide array of #1 surgeons, highly experienced with maximum guarantee of 100% positive results.
- Veteran surgeons: of surgeries in the modern times.
- Successful record: Surgery history is not new to India, and we have successfully performed over 1000s of surgeries in the modern times.
- Low costs: The achalasia cardia surgery cost and overall medical stay in India is barely 25% of what you may need to incur in western countries.
- Endless benefits: The benefits of undergoing a surgery in India are endless, with nearly 0% rate of side-effects.
- Mini vacation: India has a mystic quality of mesmerizing its visitors. You may wish for your fast treatment and recovery to get back on your feet for a vacation in the world’s #1 country with oldest cultural heritage and history.
Achalasia Cardia:
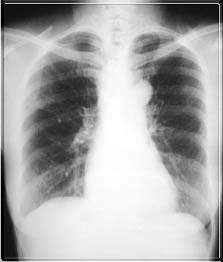 Achalasia Cardia is a primary oesophageal motility disorder, characterised by a hypertensive lower oesophageal sphincter (LOS) which fails to relax on swallowing, and by aperistalsis of the body of the oesophagus.The aetiology of the disease remains unknown. Epidemiological findings rule out an infectious cause, and there appears to be minimal genetic influence. A viral cause is plausible but as of yet electron microscopy has failed to detect viral particles in the vagus nerve or in the oesophageal intramural nerve plexus. The incidence of the disease is 1-2 per 200,000 per year, with both sexes equally affected. Onset of the disease is typically between the ages of 20 and 50.
Achalasia Cardia is a primary oesophageal motility disorder, characterised by a hypertensive lower oesophageal sphincter (LOS) which fails to relax on swallowing, and by aperistalsis of the body of the oesophagus.The aetiology of the disease remains unknown. Epidemiological findings rule out an infectious cause, and there appears to be minimal genetic influence. A viral cause is plausible but as of yet electron microscopy has failed to detect viral particles in the vagus nerve or in the oesophageal intramural nerve plexus. The incidence of the disease is 1-2 per 200,000 per year, with both sexes equally affected. Onset of the disease is typically between the ages of 20 and 50.
- Inhomogeneous cardiac density: Not demonstrable in this presentation
- Density crossing mid-line. Not demonstrable in this presentation
- Right sided inlet to outlet shadow. Not demonstrable in this presentation
- Barium swallow below: Dilated esophagus
The principal lesion is denervation of the oesophageal smooth muscle. While muscular abnormalities are also present, these appear to be secondary to the neural deficit. A decreased number of ganglion cells in the oesophageal intramural nerve plexus has been found in patients with achalasia, and the extent of this loss corresponds to the duration of the disease. There may also be degenerative changes in the vagus nerve, both in its branches to the oesophagus and in the dorsal motor nucleus. The interaction between nerve plexus and vagus nerve lesions is not yet clear. In both cases, the loss predominantly concerns inhibitory neurons. This would explain the increased basal LOS pressure as well as the inadequate sphincteric relaxation observed on swallowing. Degeneration of the oesophageal ganglion cells leads to permanent aperistalsis as the disease progresses and favours oesophageal dilatation.
Progressive dysphagia is the most common presenting symptom. It generally concerns both liquids and solids from the outset. The second most common symptom is the regurgitation of undigested food during or shortly after a meal. Approximately 36% of patients present with sub/retrosternal pain and a similar percentage with heartburn.11 Weight loss is a very common finding in patients with achalasia due to decreased food intake, and is a good indicator of the chronicity and severity of the condition. Patients may complain of nocturnal coughing if there is overspill of oesophageal contents into the trachea, which is increased in the supine position. Pulmonary infiltrates resulting from aspiration constitute a rare, but severe, complication.Diagnosis of achalasia cardia is based on history, barium swallow with fluoroscopy, upper endoscopy and oesophageal manometry.
Pseudoachalasia can occur in a number of conditions, most commonly in gastric adenocarcinoma.12 The mechanism may be infiltration of the oesophageal nerve plexus or constriction of the distal oesophagus by the tumour mass. Endoscopy can be used to rule out this differential diagnosis, which is more common among older patients, who usually present with marked weight loss. Oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma, lymphoma, lung carcinomas and a number of other malignancies can also cause pseudoachalasia. Other conditions which can mimic achalasia include Chaga’s disease, amyloidosis, sarcoidosis, oesophageal stricture, chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction and post-vagotomy disturbance.
TREATMENT
As the degenerative neural lesion of this disease cannot be corrected, treatment is directed at palliation of symptoms and prevention of complications. Effective peristalsis is rarely restored by successful treatment, but improved oesophageal emptying and a decrease in oesophageal diameter are generally expected. Four palliative treatments are available: pharmacotherapy, botulinum toxin injection, pneumatic dilatation and myotomy. They all aim to decrease LOS pressure and improve emptying by gravity.
Ms. Nina with her mother Ms. Naah Pauline from Cameroon, sharing her Mother's Experience of Gastric Achalasia Cardia Surgery done in India

Ms. Nina and her mother Ms. Naah Pauline from Cameroon
We consulted a doctor at Tour2India4Health for my mother’s because she was having difficulty in swallowing everything lately. Initially we were a bit apprehensive about straight away going for the surgical option because we thought it’s just an early stage and oral medication might work and provide her some relief. However, after we did our research and talked to the doctors, we were convinced that undergoing surgery is the most reliable option. The doctor was very skilled at performing the gastric achalasia cardiac surgery. In fact, he has always been available on calls whenever we need guidance, which really assured us of her speedy recovery.
★★★★★ Published
Pharmacotherapy :
Smooth muscle relaxants alleviate symptoms and improve oesophageal emptying in up to 70% of patients. Nitrites, such as sublingual isosorbide dinitrite, and calcium channel blockers, such as diltiazem, nifedipine and verapamil, have this effect. The role of pharmacological agents in the long-term management of achalasia is unclear. It is not known whether their long-term use prevents dilatation and complications. This treatment option is suitable for patients with medical conditions that interfere with pneumatic dilatation or myotomy. Also, patients with severe weight loss can be treated pharmacologically until a healthy nutritional status can be re-established, making them better candidates for other forms of treatment.
Botulinum Toxin:
Botulinum toxin type A is derived from the controlled fermentation of Clostridium botulinum. The toxin binds to presynaptic cholinergic neuronal receptors, is internalised, and irreversibly interferes with acetylcholine release, probably by preventing the neurotransmitter vesicle docking and fusing with the axonal membrane. Pasricha and colleagues first demonstrated the similar ability of botulinum toxin to decrease LOS basal tone and improve symptoms in patients with achalasia. An initial, beneficial response at the level of the LOS occurs in 90% of patients, but symptoms reappear within a year in many initial responders.15 Side effects of this treatment are rare, but include chest discomfort for a few days after the injection and an occasional rash.
The best use of botulinum toxin injection in achalasia is still being explored, but this seemingly safe approach with little apparent morbidity may be of great advantage when a short-term treatment response is desired.
Dilatation:
Forceful dilatation of the gastroesophageal sphincter to a diameter of approximately 3 cm is necessary to tear the circular muscle and to ensure a lasting reduction in LOS pressure. Many types of dilators have been developed for this purpose, but it is pneumatic dilators which are conventionally used today. The technique of dilatation, inflation pressure and duration of inflation varies. Water-soluble contrast material is used to detect distal oesophageal leaks. Surgical consultation is undertaken if perforation is evident. Small perforations are managed conservatively with broad-spectrum antibiotics.16 Clinical deterioration e.g. shock, sepsis, haemorrhage or a finding of free-flowing barium into the mediastinum, requires immediate thoracotomy and repair.
At least 60% of patients have a good response and success rates exceeding 95% have been reported.17 The response rate varies with patient age, (younger patients do not do as well as older patients), and duration of symptoms, (those with a shorter history do not respond as well), but it does not seem to be related to the degree of oesophageal dilatation or tortuosity. The efficacy of this procedure is decreased by as much as half with each subsequent dilatation.
Morbidity is mostly related to oesophageal perforation, a complication in approximately 5% of patients, but surgical repair is required in less than half of these cases.17 Perforation may be more likely in severely malnourished patients, which raises the possibility that re-establishment of a good nutritional status decreases the complication rate following dilatation.
Surgery:
The goal of surgical therapy in achalasia is to decrease LOS resting pressure without completely compromising its competency against gastroesophageal reflux (GOR). The Heller procedure was described in 1913 and now a modification of this procedure is used most commonly in the surgical management of achalasia.19,20 An anterior myotomy is performed by dividing the circular muscle of the oesophagus down to the level of the mucosa. The myotomy extends less than 1cm onto the stomach and to several centimetres above the palpable region of the lower sphincter. The transthoracic approach is preferred, as it helps confirm the diagnosis, allows careful palpation and inspection of the oesophagus, and enables the surgeon to extend the myotomy proximally as far as is necessary. Open myotomies have good results in 80-90% of patients.21,22 They decrease the LOS pressure more reliably, and therefore have a greater efficacy than pneumatic dilatation.
Minimally invasive surgical procedures are becoming a preferable alternative to open myotomy, allowing the Heller myotomy to be performed thoracoscopically and laparoscopically .24,25,26 Shorter hospitalisation, less pain and early resumption of activity are the benefits of the minimally invasive approach, which remains as effective as the open techniques in the relief of dysphagia.27 Complications of minimally invasive surgery include: anterior gastric perforation, mucosal perforation at the gastroesophageal (GO) junction and, most significantly, GOR. Surgery is not necessary for a patient who has few symptoms and minimal oesophageal dilatation. It is, however, required for those with dilatation and food retention to prevent serious pulmonary complications and, of course, to provide symptomatic relief.
Go to the Enquiry Form
Phone Numbers Reach Us
India & International : +91-9860755000 / +91-9371136499
UK : +44-2081332571
Canada & USA : +1-4155992537
Below are the downloadable links that will help you to plan your medical trip to India in a more organized and better way. Attached word and pdf files gives information that will help you to know India more and make your trip to India easy and memorable one.
 Apollo Hospital
Apollo Hospital Fortis Hospital
Fortis Hospital Artemis Hospital
Artemis Hospital
 Medanta Hospital
Medanta Hospital



 Jaslok Hospital
Jaslok Hospital Lilavati Hospital
Lilavati Hospital

 Global Hospitals
Global Hospitals Jupiter Hospital
Jupiter Hospital













