Neuro Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy Surgery India
Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy (PELD):
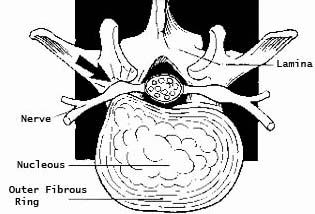 |
Percutaneous endoscopic lumbardiscectomy (PELD) is a new technique for the decompression of the lumbar disc space and removal of nucleus pulposus via a posterolateral approach. |
The technique was introduced in Germany by the authors in April 1987. The method is indicated in patients with non-equestrated lumbar disc herniation with an intact lorsal longitudinal ligament. In local anesthesia, a working cannula (OD 5 mm) is placed at the dorsal lateral border of the disc. The disc space is opened with anulus trephines and the nucleus pulposus is removed with rigid and flexible forceps as well as with automated shaver systems under intermittent endoscopic control (discoscopy). The procedure is performed in local anesthesia. The results of the first thirty patients with a follow-up time between 6 months and 17 months could be graded as excellent in 13 cases, as good in 9 cases, as fair in 6 cases, and as bad in 2 cases. The relief of symptoms as judged by the patients was between 70–100 percent in the majority of the cases. Three patients had to be reoperated at the same level and site, because of either persistent or recurrent sciatica. The performance in local anesthesia, the atraumatic extraspinal approach, the reduced time of hospitalization and post-operative morbidity as well as the reduced time of work incapability are the main advantages of this new method.
Percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy: minimally invasive, but perhaps only minimally useful?
BACKGROUND A few recent studies dampen the euphoric reports of the value of percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy (PELD) in the treatment of discogenic disease. We felt that a large-scale comparison between PELD and the still minimally invasive open lumbar disk surgery (OLDS) was called for. METHODS This report is based on the surgical experience of one year (1991) and is confined to the intervertebral disk level L4-5. Three hundred thirteen patients treated by open disk surgery were compared with 13 who were selected for percutaneous discectomy. RESULTS Using careful selection criteria, only 13 (4%) of a possible 326 were considered potentially suitable for PELD. Of these, only eight were wholly suitable and were operated on percutaneously. Within the first postoperative month, 62.5% (5 patients) of the PELD group required open surgery for definitive treatment, whereas only 14 (4%) of the 313 OLDS patients had to undergo additional surgery. CONCLUSIONS Although it may of benefit to a very few, we feel that the PELD method cannot be considered a substitute for, or even an alternative to, traditional surgery in most cases.
Neuro Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy Surgery in India is available in following cities:
| Mumbai | Hyderabad | Kerala |
| Delhi | Pune | Goa |
| Bangalore | Nagpur | Jaipur |
| Chennai | Gurgaon | Chandigarh |
Go to the Enquiry Form
Phone Numbers Reach Us
India & International : +91-9860755000 / +91-9371136499
UK : +44-2081332571
Canada & USA : +1-4155992537
Below are the downloadable links that will help you to plan your medical trip to India in a more organized and better way. Attached word and pdf files gives information that will help you to know India more and make your trip to India easy and memorable one.
 Apollo Hospital
Apollo Hospital Fortis Hospital
Fortis Hospital Artemis Hospital
Artemis Hospital
 Medanta Hospital
Medanta Hospital



 Jaslok Hospital
Jaslok Hospital Lilavati Hospital
Lilavati Hospital

 Global Hospitals
Global Hospitals Jupiter Hospital
Jupiter Hospital













