Shoulder Joint Replacement Surgery in India
Definition
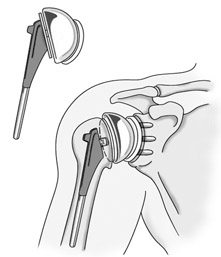 Shoulder joint replacement surgery is performed to replace a shoulder joint with artificial components (prostheses) when the joint is severely damaged by such degenerative joint diseases as arthritis, or in complex cases of upper arm bone fracture
Shoulder joint replacement surgery is performed to replace a shoulder joint with artificial components (prostheses) when the joint is severely damaged by such degenerative joint diseases as arthritis, or in complex cases of upper arm bone fracture
Purpose
The shoulder is a ball-and-socket joint that allows the arms to be raised, twisted, bent, and moved forward, to the side and backward. The head of the upper arm bone (humerus) is the ball, and a circular cavity (glenoid) in the shoulder blade (scapula) is the socket. A soft-tissue rim (labrum) surrounds and deepens the socket. The head of the humerus is also covered with a smooth, tough tissue (articular cartilage); and the joint, also called the acromioclavicular (AC) joint, has a thin inner lining (synovium) that facilitates movement while surrounding muscles and tendons provide stability and support. The AC joint can be damaged by the following conditions to such an extent as to require replacement by artificial components:
Arthritis in Africa
and Why African Patients Travel To India for Its Treatment 
 Phone / Whatsapp : +91-9371136499
Phone / Whatsapp : +91-9371136499
Osteoarthritis. This is a degenerative joint disease characterized by destruction or thinning of the articular cartilage. When non-surgical treatment is no longer effective and shoulder resection not possible, joint replacement surgery is usually indicated.
Rheumatoid arthritis. Shoulder replacement surgery is the most commonly performed procedure for the arthritic shoulder with severe inflammatory or rheumatoid arthritis.
Severe fracture of the humerus. A fracture of the upper arm bone can be so severe as to require replacement of the AC joint.
Osteonecrosis. This condition usually follows a three- or four-part fracture of the humeral head that disrupts the blood supply, resulting in bone death and disruption of the AC joint.
Charcot's arthropathy. Also called neuropathic arthropathy or arthritis, Charcot's arthropathy is a condition in which the shoulder joint is destroyed following loss of its nerve supply.
Demographics
Shoulder arthritis is among the most prevalent causes of shoulder pain and loss of function. In the United States, arthritis of the shoulder joint is less common than arthritis of the hip or knee. Individuals with arthritis in one joint are more likely to get it in another joint. Overall, arthritis is quite common in the United States, affecting about 16 million Americans. Osteoarthritis is also the most common joint disorder, extremely common by age 70. Men and women are equally affected, but onset is earlier in men.
Description
Shoulder joint replacement surgery can either replace the entire AC joint, in which case it is referred to as total shoulder joint replacement or total shoulder arthroplasty; or replace only the head of the humerus, in which case the procedure is called a hemiarthroplasty.
Implants
The two artificial components that can be implanted in the shoulder during shoulder joint replacment surgery are:
The humeral component. This part replaces the head of the humerus. It is usually made of cobalt or chromium-based alloys and has a rounded ball attached to a stem that can be inserted into the bone. It comes in various sizes and may consist of a single piece or a modular unit.
The glenoid component. This component replaces the glenoid cavity. It is made of very high-density polyethelene. Some models feature a metal tray, but the 100% polyethylene type is more common.
Shoulder joint replacement surgery is performed under either regional or general anesthesia, depending on the specifics of the case. The surgeon makes a 3-4 in (7.6-10.2 cm) incision on the front of the shoulder from the collarbone to the point where the shoulder muscle (deltoid) attaches to the humerus. The surgeon also inspects the muscles to see if any are damaged. He or she then proceeds to dislocate the humerus from the socket-like glenoid cavity to expose the head of the humerus. Only the portion of the head covered with articular cartilage is removed. The center cavity of the humerus (humeral shaft) is then cleaned and enlarged with reamers of gradually increasing size to create a cavity matching the shape of the implant stem. The top end of the bone is smoothed so that the stem can be inserted flush with the bone surface.
If the glenoid cavity of the AC joint is not damaged and the surrounding muscles are intact, the surgeon does not replace it, thus performing a simple hemiarthroplasty. However, if the glenoid cavity is damaged or diseased, the surgeon moves the humerus to the back and implants the artificial glenoid component as well. The surgeon prepares the surface by removing the cartilage and equalizes the glenoid bone to match the implant. Protrusions on the polyethylene glenoid implant are then fitted into holes drilled in the bone surface. Once a precise fit is achieved, the implant is cemented into position. The humerus, with its new implanted artificial head, is replaced in the glenoid socket. The surgeon reattaches the supporting tendons and closes the incision.
Diagnosis/Preparation
Damage to the AC joint is usually assessed using x rays of the joint and humerus. They provide information on the state of the joint space, the position of the humeral head in relation to the glenoid, the presence of bony defects or deformity, and the quality of the bone. If glenoid wear is observed, a computed tomography (CT) scan is usually performed to evaluate the degree of bone loss.
The treating physician usually performs a general medical evaluation several weeks before shoulder joint replacement surgery to assess the patient's general health condition and risk for anesthesia. The results of this examination are forwarded to the orthopedic surgeon, along with a surgical clearance. Patients are advised to eat properly and take a daily iron supplement some weeks before surgery. Several types of tests are usually required, including blood tests, a cardiogram, a urine sample, and a chest x ray. Patients may be required to stop taking certain medications until surgery is over.
Aftercare
Following surgery, the operated arm is placed in a sling, and a support pillow is placed under the elbow to protect the repair. A drainage tube is used to remove excess fluid and is usually removed on the day after surgery.A careful and well-planned rehabilitation program is very important for the successful outcome of a shoulder joint replacement. It should start no later than the first postoperative day. A physical therapist usually starts the patient with gentle, passive-assisted range of motion exercises. Before the patient leaves the hospital (usually two or three days after surgery), the therapist provides instruction on the use of a pulley device to help bend and extend the operated arm.
Risks
Complications after shoulder replacement surgery occur less frequently than with other joint replacement surgeries. However, there are risks associated with the surgery such as infection; intra-operative fracture of the humerus or postoperative fractures; biceps tendon rupture; and postoperative instability and loosening of the glenoid implant. Advances in surgical techniques and prosthetic innovations are helping to significantly lower the occurrence of complications.
Normal results
Pain relief is expected after shoulder joint replacement because the diseased joint surfaces have been replaced with smooth gliding surfaces. Improved motion, however, is variable and depends on the following:
The surgeon's ability to reconstruct the shoulder's supporting tissues, namely the shoulder ligaments, capsule, and muscle attachments.
The patient's preoperative muscle strength.
The patient's motivation and compliance in participating in postoperative rehabilitation therapy.
Below are the downloadable links that will help you to plan your medical trip to India in a more organized and better way. Attached word and pdf files gives information that will help you to know India more and make your trip to India easy and memorable one.
Go to the Enquiry Form
Phone Numbers Reach Us
India & International : +91-9860755000 / +91-9371136499
UK : +44-2081332571
Canada & USA : +1-4155992537
 Apollo Hospital
Apollo Hospital Fortis Hospital
Fortis Hospital Artemis Hospital
Artemis Hospital
 Medanta Hospital
Medanta Hospital



 Jaslok Hospital
Jaslok Hospital Lilavati Hospital
Lilavati Hospital

 Global Hospitals
Global Hospitals Jupiter Hospital
Jupiter Hospital













